Urbanization
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews
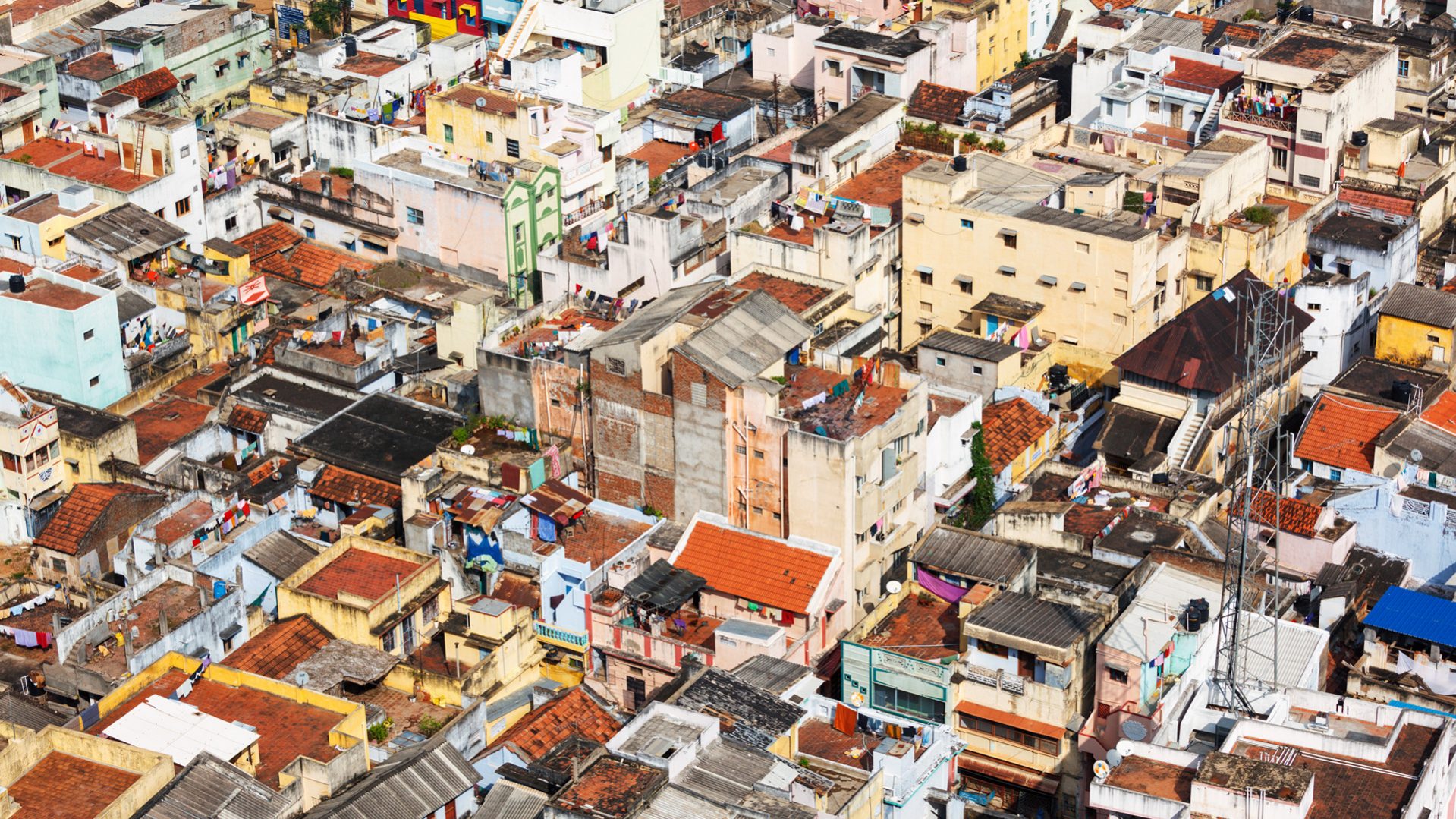

Urbanisation
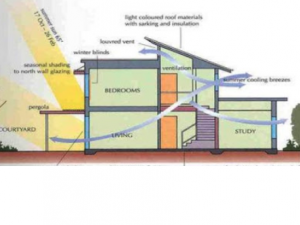
Urbanization is a form of social transformation from traditional rural societies to modern urban communities. It is long term continuous process.
It can be defined as, “as a process which reveals itself through temporal, spatial and sectoral changes in the demographic, social, economic, technological and environmental aspects of life in a given society. Urbanization is a Progressive concentration of population in urban unit (Kingsley Davis-1965). These changes manifest themselves in the increasing concentration of popuation in human settlements, larger than villages, in the increasing involvement of the people in the secondary and tertiary production functions, and in the progressive adoption of certain social traits which are typical of traditional rural societies.”
Urbanization accompanies industrialization, and is also interlinked with modernization. In the developed countries the process of urbanisation has been slow but steady, accompanied by industrial and agricultural revolutions. Whereas in the developed countries urbanisation has been a rapid process not linked to agricultural or industrial growth but to the growth of the service sector.
In the third world countries urbanisation has not been accompanied by industrialisation or modernisation.
It is pertinent to identify the main issues which are related to urbanisation. These are economic, demographic, social, cultural and political.