Traditional and Vernacular systems
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews
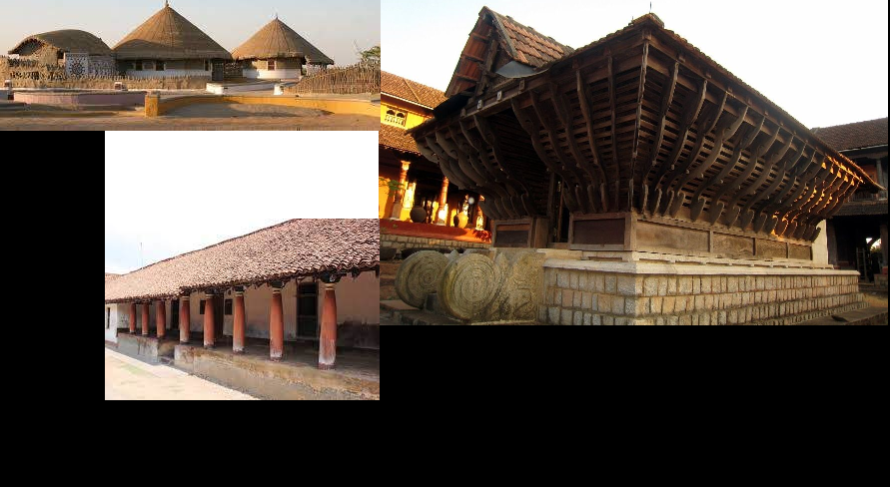

Geography
Hilly Region
In hilly country where rocky rubble, ashlars, and pieces of stone, these can be patched together with a mud mortar to form walls. Finer stonework veneer covers the outside. Sometimes wood beams and rafters are used with slate tiles for roofing if available. The roof is pitched to deal with the heavy rains and snowfall.
Flatlands
Earth or mud construction is seen in the flatlands, Houses are usually made of mud or sun-baked bricks, then plastered inside and out. Sometimes with mud mixed with hay or even cow dung and whitewashed with lime. Where bamboo is available (mainly in the north and northeastern states) it is widely used for all parts of the home as it is flexible and resilient. Also widely used is thatch from plants such as elephant grass, paddy, and coconut. In the south, clay tiles are used for roofing while various plant material such as coconut palm is common for low-cost buildings.
Climate
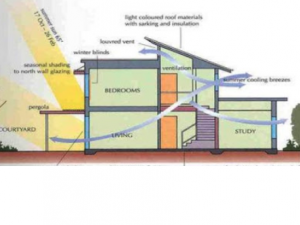
As climate decides the parameters for comfort within a built form . It also influences the choice of materials used for construction.
Indigenous Materials
The most important aspect influencing the development of vernacular construction practices is the availability of local building materials. In many areas, the local resources have governed the use of the following constituent materials for walls: • Adobe (mud blocks or whole walls) • Masonry (stone, clay, or concrete blocks) • Timber