Timber Roofs
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews

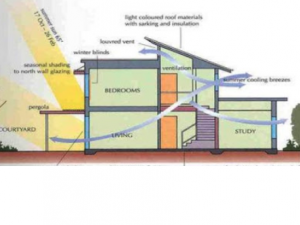
Roof is an important element in providing protection from weather and has a significant role to play in the reduction of heat loss from a building.Roofs are classified as either pitched or flat. Timber is the most common material used for pitched roofs. Concrete is universally used for flat roofs. Timber roof construction is the oldest and the traditional technique of construction of roofs.
The roof should be well designed and constructed to meet the requirements of different climates and the covering material available. Pitched roofs are said to be more suitable in coastal regions where rainfall is heavy and flat roofs are suitable in regions with scanty rainfall and high temperatures.
The roofs may be classified as follows:
Pitched roof:
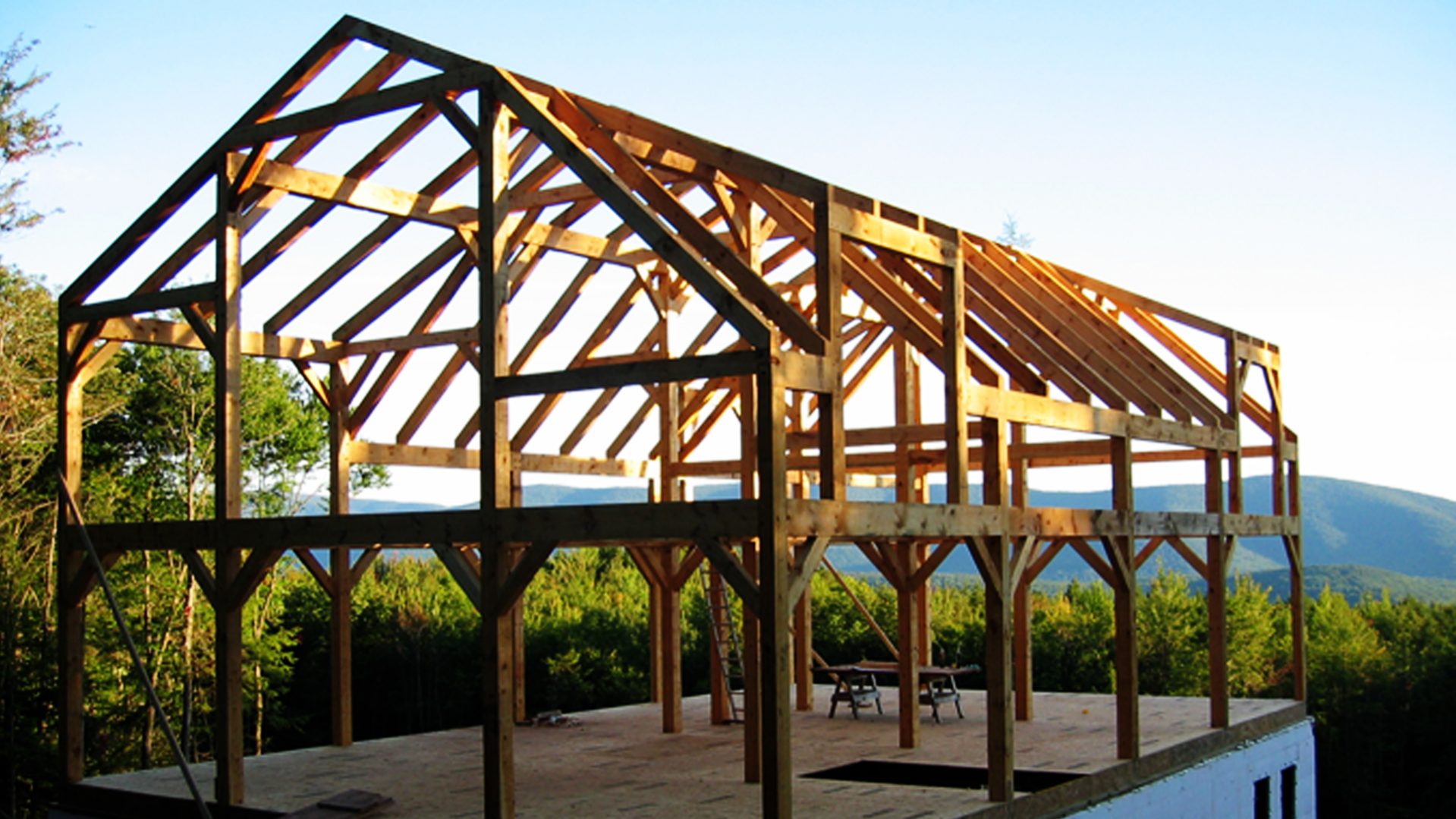
A pitched roof is a roof comprising a sloping surface or surfaces with an angle of usually over 20 degrees. It is a bi-fold, bi-planer roof with a ridge at its highest point. To be more specific – a pitched roof requires a pitch of more than 10 degrees or a roof with two slopes that meet at a central ridge.
Pitched roofs offer a more classical appearance. They remain the most common and efficient solution in wet and cold weathers to ensure maximum protection.
Flat roofs:
A roof which is approximately horizontal is called a flat roof. It is becoming more popular with the introduction of suitable building materials. it may be constructed in reinforced cement concrete, flagstone supported on rolled Steel joist, bricks, concrete or tiled arches. This roof is provided with a slight slope in one direction to drain of the rainwater easily. The construction of flat roof is similar to the construction of floor except that the top surface is protected against rainwater.
Shell roofs:
Shell roofs are very useful for covering large structures, e.g; assembly halls, recreation centres, libraries, theatres, and factories. RCC shell roofs are becoming very popular these days. Very less quantity of material are required to build up a shell roof as compared to other conventional method of roofing for the same span. The design of the shell is made as thin as practical requirements will allow, such that the dead load is decreased and the Shell acts as a membrane free from large bending stresses. Least quantity of materials is used to maximum structural advantage.
Domes:
A Dome is a special type of Shell roof of semi spherical or semi elliptical shape. The modern thin shell dome may be considered as an evolution of a structural form known and used by man from ancient ages. Dome structures may be divided into two main divisions: Smoothed shell domes and Ribbed domes. Smooth shell domes may be divided into domes with shells of uniform thickness and domes with shells of uniformly varying thickness