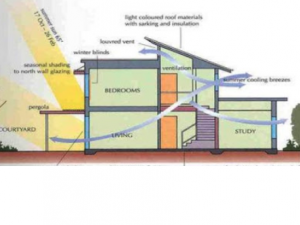
Sewage disposal
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews
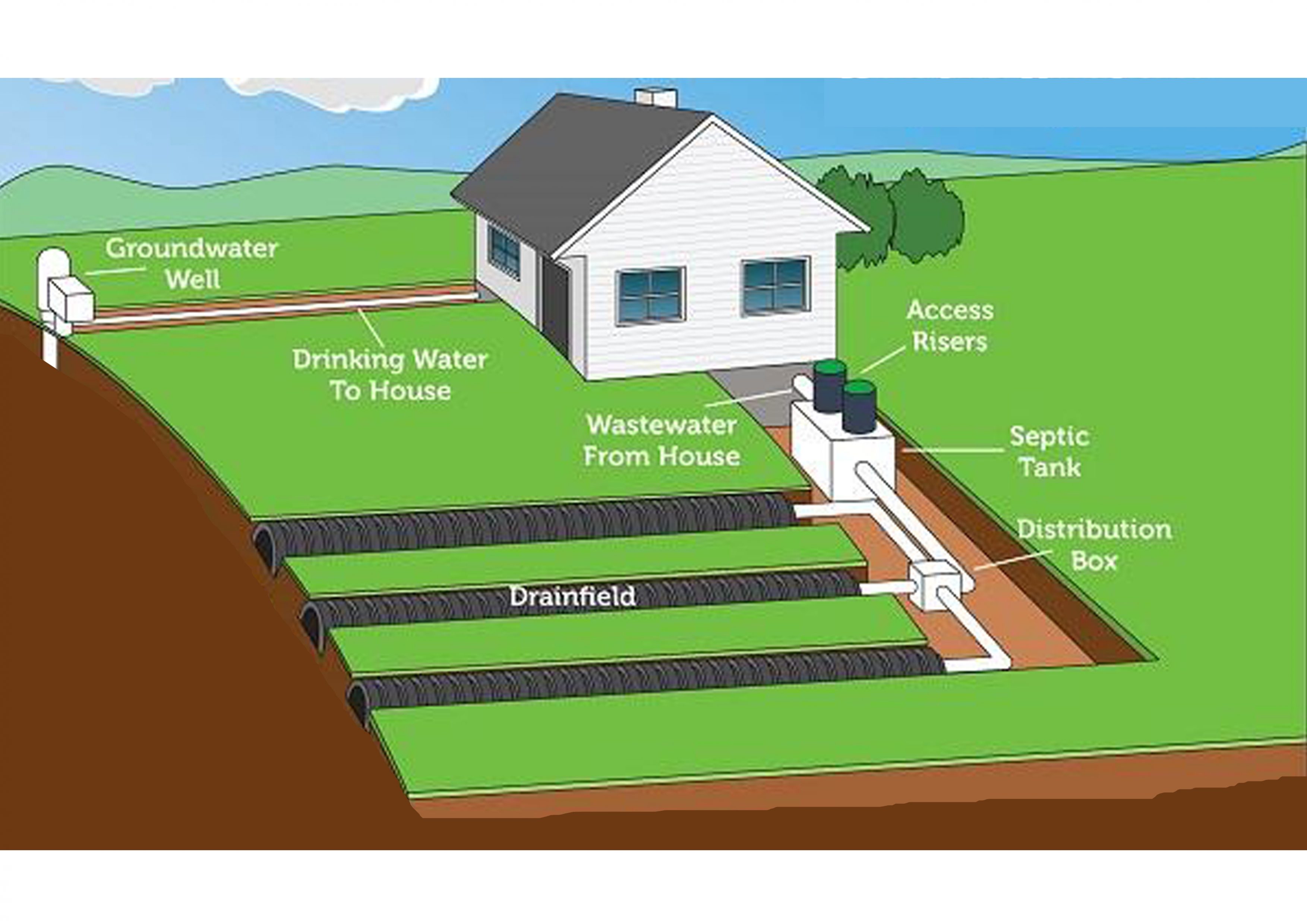
On-site sanitation:
In this system, wastewater is contained at the point of generation. Septic tank, pit and soak pit toilets and eco-sanitation toilets that do not require sewer/transportation, etc are types of on-site sanitation systems.
The septage in the septic tank is transported through mechanical means at frequent intervals.
Off-site sanitation:
Transportation of wastewater to another location for disposal is done along with treatment or reuse of this wastewater is termed as off-site sanitation systems.
Normally, such systems require a sewer system or mechanical transportation of waste. The off-site sanitation can be centralized (at a single point in town/village) or decentralized ( at communal level).
Ecological sanitation
This is a form of sanitation which involves the reuse of human faecal waste/ wastewater and its nutrient back into the local environment, thus avoiding pollution of land, air, and water resources. The system involves the treatment of human faecal waste and wastewater and reuse of the treated products. The system produces two types of products:
a. Manure for agricultural use.
b. Treated water that can be used in agriculture or gardening, flushing in toilets and aquaculture.
There are two major categorization of liquid waste/domestic wastewater:
1. Grey Water:
Wastewater generated from bathing, washing, general cleaning, laundry, as well as from community stand post, well, hand pumps, etc.
2. Black Water:
Wastewater generated from a toilet containing faecal matter. Such water contains a very high amount of pathogen compared to greywater.
Grey and black water can be collected separately and treated/disposed of separately, as greywater does not require very high treatment as black water. However, both can be collected and treated/disposed of together.
Liquid waste also comprise of Yellow Water (urine with or without flush water). It is separated in certain types of toilet units and reused as fertilizer.
• Once the waste is collected in the pit, septic tank, etc., it further disintegrates and can be termed as follow:
a. Sludge: It is the settled solid matter in the semi-solid condition in any collection/storage system. The term sewage sludge is generally used to describe residuals from centralized wastewater treatment, while the term septage is used to describe the residuals from septic tanks. Solids or settled content in pit latrines and septic tanks are also called faecal sludge.
b. Scum: Impure matter like oil, hair, grease, and other light material that float at the surface of the liquid in the septic tank.
c. Effluent: Wastewater that flows out of a treatment system (septic tank in this module). It is partially treated.