Physics of Light and Visual Comfort
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews

Artificial Light
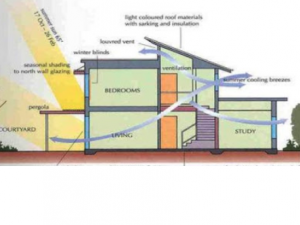
Architects design spaces which are closed, semi-closed or/and open. While designing these spaces, Considerations for various parameters for a good lighting design solution are important. Visual comfort is a very important consideration
Modern theory of light and colour
How is Light Transmitted?
Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation perceptible to the human eye. It is made out of photons. Photons behave like particles in some ways and like waves in other ways. If a beam of light is shined at a mirror, for example, it bounces off of it just like a ball would. If light is shining through a narrow slit, however, the light fans out like a wave would. It appears that light is neither a wave nor a particle, but something unusual with characteristics of both.
Frequencies
One of the wave-like properties of light is frequency. The frequency is how fast a photon of light vibrates. The frequency determines the colour; high-frequency light is violet in colour, whereas lower frequency light is red. Frequency is inversely proportionate to wavelength–the higher the frequency, the shorter the waves. Radio waves, gamma waves and other electromagnetic waves work in much the same way that light does, but they have frequencies too high or low for the eye to see.
Transmitting Light
Although light can travel through a vacuum, it cannot travel through all objects. When light strikes an object, it can be transmitted, reflected or absorbed. The object is made of molecules, and each molecule has electrons, capable of jumping to higher energy levels by absorbing energy. A light packet has a certain amount of energy in it according to its frequency– the higher the frequency, the more energy. If this energy corresponds to one of the electron energy levels, the electron will absorb it and re-emit it as heat. Transparent materials, however, do not absorb the energy of the photon. Since the photon is not absorbed, it can pass straight through. Some materials are partially transparent, absorbing some photons and transmitting others. This will make the material look tinted since it only passes certain colours of light.