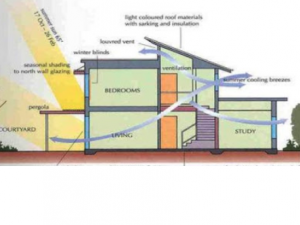
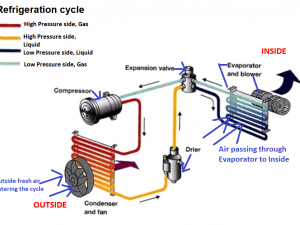
Design movements from : 1940 to 1970
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews

The instability created in Europe by the First World War (1914-18) set the stage for another international conflict–World War II–which broke out two decades later and was more devastating. Rising to power in an economically and politically unstable Germany, Adolf Hitler Adolf Hitler, leader of the Nazi Party, rearmed the nation and signed strategic treaties with Italy and Japan to further his ambitions of world domination. Hitler’s invasion of Poland in September 1939 drove Great Britain and France to declare war on Germany, marking the beginning of World War II. Over the next six years, the conflict would take more lives and destroy more land and property around the globe than any previous war. Among the estimated 45-60 million people killed were 6 million Jews murdered in Nazi concentration camps.
The Effects of World War II on Europe
The Second World War (WWII) was one of the major transformative events of the 20th century, with 39 million deaths in Europe alone. Large amounts of physical capital were destroyed through six years of ground battles and bombing. Many individuals were forced to abandon or give up their property without compensation and to move on to new lands. Periods of hunger became more common even in relatively prosperous Western Europe. Due to WWII, political and economic systems in many countries were permanently altered. The role of architecture played an important role in shaping the post war world.