Colonial Architecture in India till 1857
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews
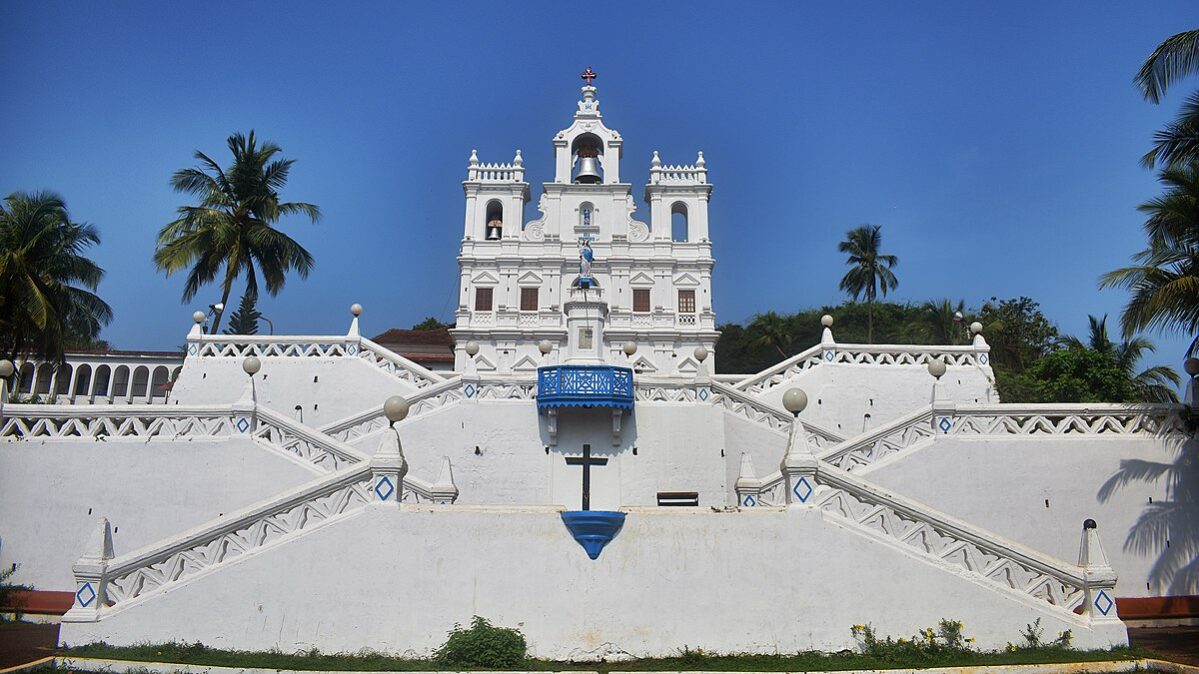

A brief history of colonization in India: various colonial powers like the Dutch, the Portuguese, the French and British reached India for trade and settled in different parts in India. Like all other aspects of society, the colonization of India also had a great impact on architecture. Colonization marked a new chapter in Indian architecture.
World Colonization
By the end of the 17th century, sea voyage to distant lands had begun in search of less expensive spices developed into a struggle among the various European nations for control of foreign lands and their lucrative trading links. The principal competitors were Portugal, Spain, Holland, France, and Britain. The models of colonization differed according to circumstance.
The primary form of colonial intervention was the founding of plantations, which had to be managed with a firm grip. Their principal commodities were sugar, coffee, tobacco, cocoa, and tea. The plantation system was first installed by the Dutch in Indonesia, the Spanish in the Americas, and the French in the Caribbean— and then eventually in Africa itself.
The situation in New England was different; the initial impetus for colonialization was economic.
By 1700, from Maine to Virginia villages and towns had a mixture of Dutch and English Puritans, French Calvinists, Catholics, Swedes, Spanish Jews, and English Anglicans. By the early 1700s, a traveller would have found courthouses, schools, churches, roads, and two universities— Harvard, founded in 1636, and Yale, founded in 1701. New England was an international mercantile-agrarian project, unique in the colonial world.